What are the typical applications of CCA PV ribbon in solar modules?
CCA PV ribbon, as a cost-effective alternative to pure copper ribbon, is widely used in solar module manufacturing with applications that align with its core functions of current conduction and interconnection, while maintaining compatibility with standard production processes. Its typical applications are mainly divided into two categories based on the module’s internal current transmission needs:
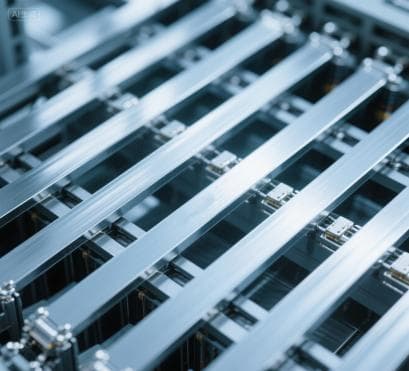
1. Tabbing Ribbon Application (Cell-Level Interconnection)
This is the most basic and high-volume application of CCA PV ribbon, focusing on connecting individual solar cells into small units.
Core Function: Establish electrical connections between adjacent solar cells (e.g., from the positive electrode of one cell to the negative electrode of the next) to form a “cell string” and transmit the direct current (DC) generated by each cell.
Target Components: Monocrystalline/polycrystalline solar cells of common sizes (166mm, 182mm, 210mm, etc.).
Key Requirements Met by CCA:
The thin copper cladding (typically 0.03–0.08mm) ensures reliable soldering to the cell’s silver grid lines, avoiding poor contact.
Its lightweight property (vs. pure copper) reduces mechanical stress on fragile cells
during soldering and handling, lowering cell breakage rates.
Typical Size for This Application: Cross-section of 0.18–0.25mm (thickness) × 1.2–2.0mm (width), matching the narrow grid lines of solar cells.
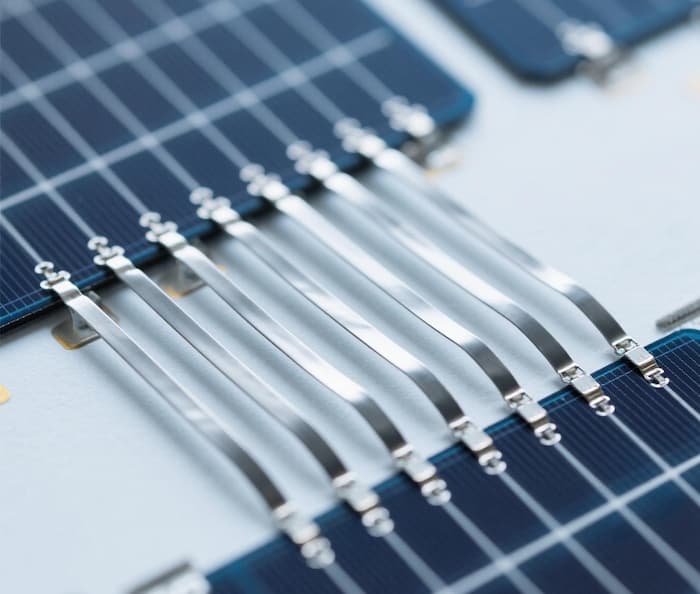
2. Busbar Ribbon Application (String-Level Current Collection)
After multiple cells are connected into strings, CCA PV ribbon acts as a busbar to aggregate current from multiple strings, serving as a “current collector” for the entire module.
Core Function: Collect the DC current output from 3–6 parallel cell strings (depending on module design) and transmit it to the module’s junction box (where it connects to the bypass diode and output cables).
Target Components: Solar cell strings (e.g., 10–12 cells per string in a 60-cell/72-cell module) and the module’s junction box.
Key Requirements Met by CCA:
Sufficient cross-sectional area (thicker/wider than tabbing ribbon) ensures low resistance, avoiding excessive power loss during current aggregation.
Compatibility with existing stringing machines: No modifications to production lines are needed, as its size and soldering performance match pure copper busbar ribbon.
Typical Size for This Application: Cross-section of 0.30–0.50mm (thickness) × 4.0–6.0mm (width), balancing current-carrying capacity and cost.
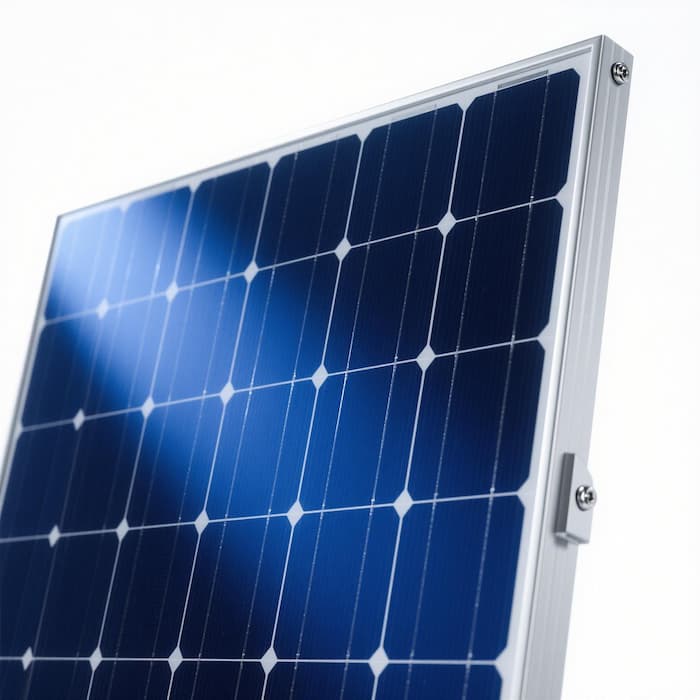

3. Supplementary Application: Special Module Designs
Beyond standard tabbing and busbar uses, CCA PV ribbon is also applied in customized or high-power module designs, where cost and weight optimization are critical:
High-Power Modules (≥500W): Used as thickened busbar ribbon (e.g., 0.50mm thickness) to handle higher current loads from large-size cells (210mm) without increasing material costs significantly.
Bifacial Solar Modules: Its corrosion-resistant design (with uniform copper cladding) ensures reliability in dual-sided exposure scenarios (e.g., humid or high-temperature environments), where ribbon durability directly affects module lifespan.
Lightweight Modules (e.g., for rooftop or mobile applications): The lower density of CCA (vs. pure copper) contributes to reducing the overall module weight by 5–8%, easing installation and transportation for weight-sensitive projects.


